La Niña is a natural climate event that brings cooler-than-normal sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. It is a part of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, alternating between warmer (El Niño) and cooler (La Niña) ocean phases. This cooling phase significantly impacts global weather patterns, especially during the winter season. In this blog, we’ll explore how La Niña influences winter weather across different regions, the science behind it, its historical effects, and what its arrival could mean for the coming months.
Impact on Winter Weather
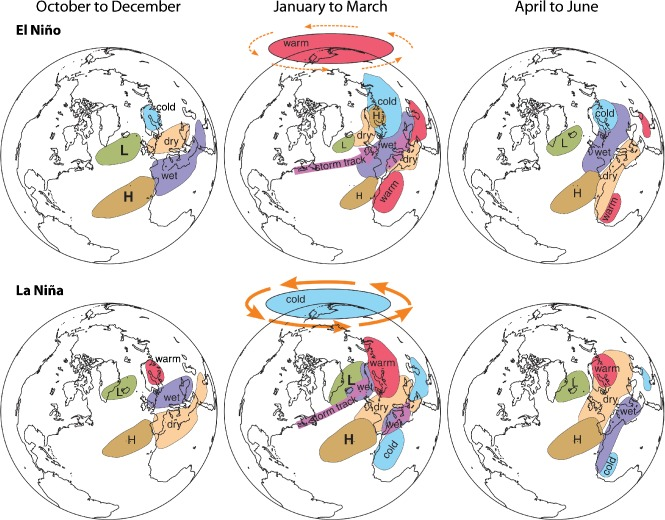
La Niña’s effects on winter weather vary by region, creating a mix of colder, wetter, and drier conditions depending on geographic location:
1. North America
- La Niña typically brings colder and snowier winters to the northern parts of the U.S. and Canada, especially in the Pacific Northwest and the Great Lakes region.
- The Southern U.S., on the other hand, often experiences drier and warmer conditions during La Niña winters, increasing the risk of drought in states like California, Texas, and Florida.
2. Europe
- La Niña’s influence in Europe is less direct but can still affect weather patterns. Northern Europe may experience colder and drier conditions, while Southern Europe could see wetter weather, particularly in the Mediterranean region.
- The altered jet stream patterns could also lead to more intense storms in the United Kingdom and Ireland.
3. Asia
- In Southeast Asia, La Niña tends to cause increased rainfall, leading to a higher risk of flooding in countries like Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines.
- In South Asia, the monsoon season may extend longer than usual, resulting in above-average rainfall in countries like India, Bangladesh, and Pakistan.
Scientific Explanation
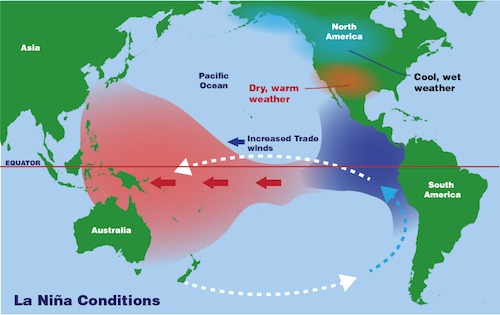
La Niña affects atmospheric conditions by altering wind patterns and air pressure. Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
- Colder sea temperatures in the Pacific Ocean intensify the trade winds that blow from east to west.
- This intensification pushes warm surface waters westward, causing cooler water to rise to the surface in the eastern Pacific.
- The result is a shift in the jet stream—a narrow band of strong winds that flow from west to east—causing changes in temperature and precipitation patterns across continents.
Historical Context

La Niña events have occurred multiple times in the past, each bringing its own set of challenges:
- 2010-2012 La Niña: This was one of the strongest La Niña events recorded. It brought severe drought to Texas and the Southern U.S., while Australia experienced major flooding.
- 2016-2017 La Niña: This event was relatively mild, leading to moderate weather changes, such as wetter conditions in Southeast Asia and drier conditions in South America.
The current La Niña forecast suggests a moderate event, potentially leading to a mix of weather outcomes similar to past occurrences. However, each La Niña has its unique dynamics influenced by other global climate factors, so exact predictions can vary.
Future Implications

The potential arrival of La Niña could have several consequences for agriculture, water resources, and disaster preparedness:
- Agriculture
- In regions where La Niña brings increased rainfall, crops might benefit from better water availability. However, excessive rain can also damage crops, delay harvests, and cause waterlogging.
- Drier areas, like the Southern U.S. and parts of South America, might face drought conditions, making irrigation essential to support agriculture.
- Water Resources
- La Niña could improve water supplies in areas prone to drought, but it could also increase the risk of flooding where rainfall becomes excessive.
- Effective water management and infrastructure development will be critical to handle potential surpluses or shortages.
- Disaster Preparedness
- With an increased likelihood of extreme weather events such as floods, landslides, and storms, governments and communities should enhance disaster response plans.
- Early warning systems, emergency evacuation plans, and community awareness campaigns can help minimize potential damage.
Conclusion
The arrival of La Niña can significantly impact global winter weather patterns, bringing both challenges and benefits. Its effects on agriculture, water resources, and disaster preparedness highlight the need for proactive planning. By understanding La Niña’s potential impacts and drawing lessons from past events, individuals and communities can better prepare for this natural phenomenon.
Communities can take practical steps like monitoring weather forecasts, planning water usage, and strengthening disaster preparedness to reduce potential risks. Stay informed and prepared to adapt to the changing weather conditions that La Niña may bring this winter.